Design of pump suction and discharge ports plays a critical role in the performance and efficiency
The design of pump suction and discharge ports plays a critical role in the performance and efficiency of the LiBr absorption units used in Hope Deepblue's systems. Here's a breakdown of the considerations for the pipeline sizing, and how it impacts the overall operation:
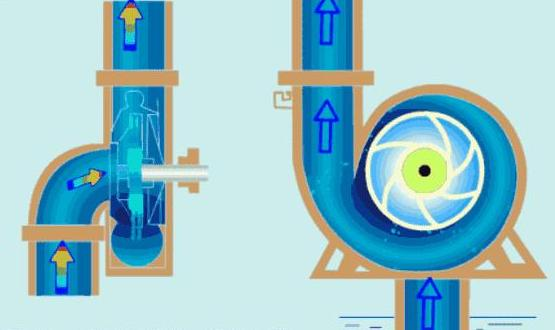
1. Suction Port vs. Outlet Diameter
- Suction Port:
The suction port is generally larger than the outlet due to the following reasons:- Low Pressure: The suction port operates at low pressure, and water density is lower, leading to slower flow rates.
- Prevent Cavitation: A larger diameter helps maintain the correct inlet pressure head, reducing the risk of cavitation (air bubbles forming and damaging the pump).
- Water Supply Balance: The larger diameter ensures a steady and sufficient water supply to the pump, maintaining efficient pump operation.
- Outlet Port:
The outlet port is generally smaller:- Higher Flow Rate: Water flows at a higher rate through the outlet due to the pressure differences, making a smaller diameter suitable for maintaining high flow velocities without compromising pump efficiency.
- Pressure Stability: A smaller diameter outlet helps maintain the pump’s output pressure and enhances system stability.
2. Importance of Reducing Pipeline Resistance
- The pipeline diameter increase can significantly reduce the fluid flow rate in the pipeline, which in turn reduces the resistance drop. This results in:
- Reduced Power Consumption: Lower resistance translates to less energy needed to move the fluid, improving overall system efficiency and reducing energy costs.
- Efficient Flow Control: Maintaining the right diameter helps in optimizing the pump’s performance by managing the flow rate and pressure effectively.
3. Cost Considerations for Larger Diameter Pipelines
- Cost vs. Efficiency:
Increasing the diameter of the pipeline raises the cost of the pipeline investment, which must be weighed against the efficiency benefits of reducing resistance and power consumption. It’s important to consider these trade-offs carefully.- For long-distance pipelines, it may be beneficial to increase the diameter to reduce resistance.
- For short-distance pipelines, it may not be necessary to increase the diameter, as the efficiency gains may not justify the additional cost.
4. Balancing the System Design
- The decision to adjust pipeline diameters depends on the overall design of the LiBr absorption unit system:
- For long-distance fluid transport, increasing the diameter can improve performance by reducing energy loss due to friction.
- For short distances, maintaining the existing diameter could be sufficient, minimizing additional costs while still maintaining system efficiency.
Conclusion
To ensure the stability and efficiency of the LiBr absorption units, a careful balance must be struck between pipeline diameter (to manage fluid flow and reduce resistance) and cost (as larger diameters come with higher initial investments). The design approach of Hope Deepblue accounts for these factors, ensuring optimized performance while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Post time: Oct-18-2024





